What Is Backflow ?
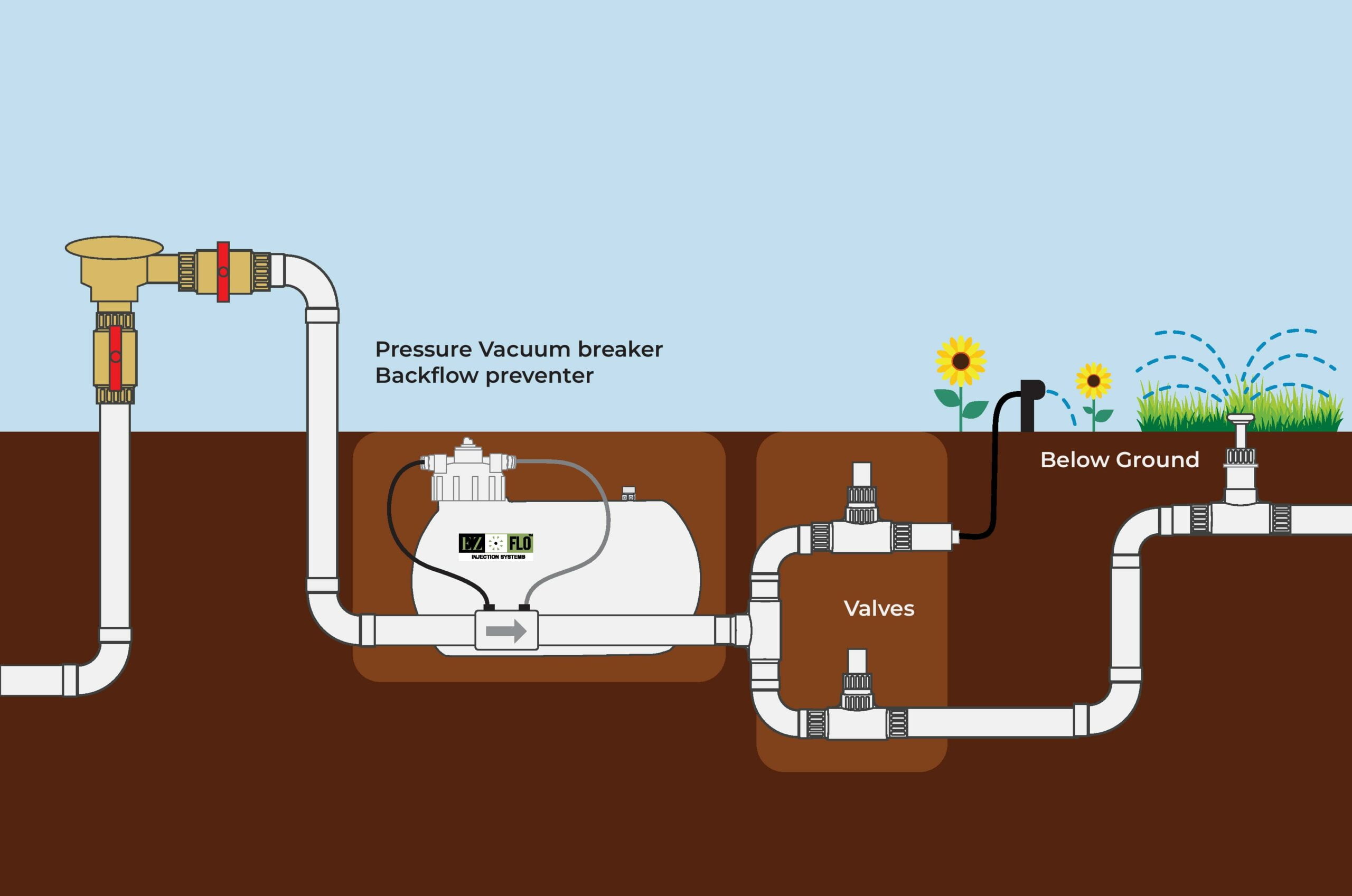
Backflow is defined as the undesirable reverse flow that returns contaminated water from a worksite to a clean water source. It can alter the pH level of the pure water source and lead to corrosion in industrial equipment if it occurs. Backflow happens in water supply systems where water is held at a sufficiently high pressure to allow it to flow backward from a faucet or nozzle.
Water pipeline systems may incorporate backflow preventers, also known as backflow prevention valves. These devices are specially designed to prevent unwanted water containing pollutants such as bacteria, contaminants, or chemicals from entering the pure drinking water source. Backflow preventer devices are attached to the steel coil plate water pipeline to stop the reverse flow of impurities.
Various types of backflow prevention valves are available on the market, including:
- Double-check backflow prevention devices
- Wastewater backflow prevention devices
- Residential backflow prevention devices
In addition to backflow preventers, the simplest and most reliable way to prevent backflow is to provide an air gap (vertical gap) between any device connected to the plumbing system and any location where contaminated water can be collected.
Cross-Connections
Cross-connections pose a risk as they provide a gateway for backflow. Backflow, the reverse flow of contaminants from “dirty” water into the safe water stream, renders the water unsafe. Backsiphonage is one way backflow occurs, creating a vacuum in the system that sucks contaminants back into the safe water flow due to a pressure change. To mitigate this, Food Code regulations mandate licensed/certified plumbers to install vacuum breakers. These breakers seal the water supply line when there’s no water flow. Other backflow prevention devices include double-check valves and reduced pressure zone backflow preventers. Regular inspection and maintenance by qualified technicians are essential to ensure their proper functioning, like any other equipment in your facility.
Which Method Will Prevent Backflow ?
An air gap stands as an infallible measure against backflow, establishing a physical separation between a safe water outlet and a potentially unsafe water source. Taking a sink as an example, the faucet should not only be positioned above the flood rim but also maintain adequate space between the sink’s drain and the floor drain.
In the event of a water supply interruption in your operation, a swift assessment is crucial to determine its impact on food safety. Cross-connections, breakdowns in water treatment facilities, or contamination detected in a private well are potential contributors to unsafe water. If the water loss poses a substantial risk to food safety, operations must halt immediately, and the regulatory authority should be promptly notified. Resuming operations after addressing the issue requires approval from the regulatory authority once the emergency has been resolved.